Discover the versatile uses and health benefits of coconut oil for beauty and wellness. Explore how it can enhance your daily routine—read more now!
Antibacterial Hand Soap or Regular Soap?
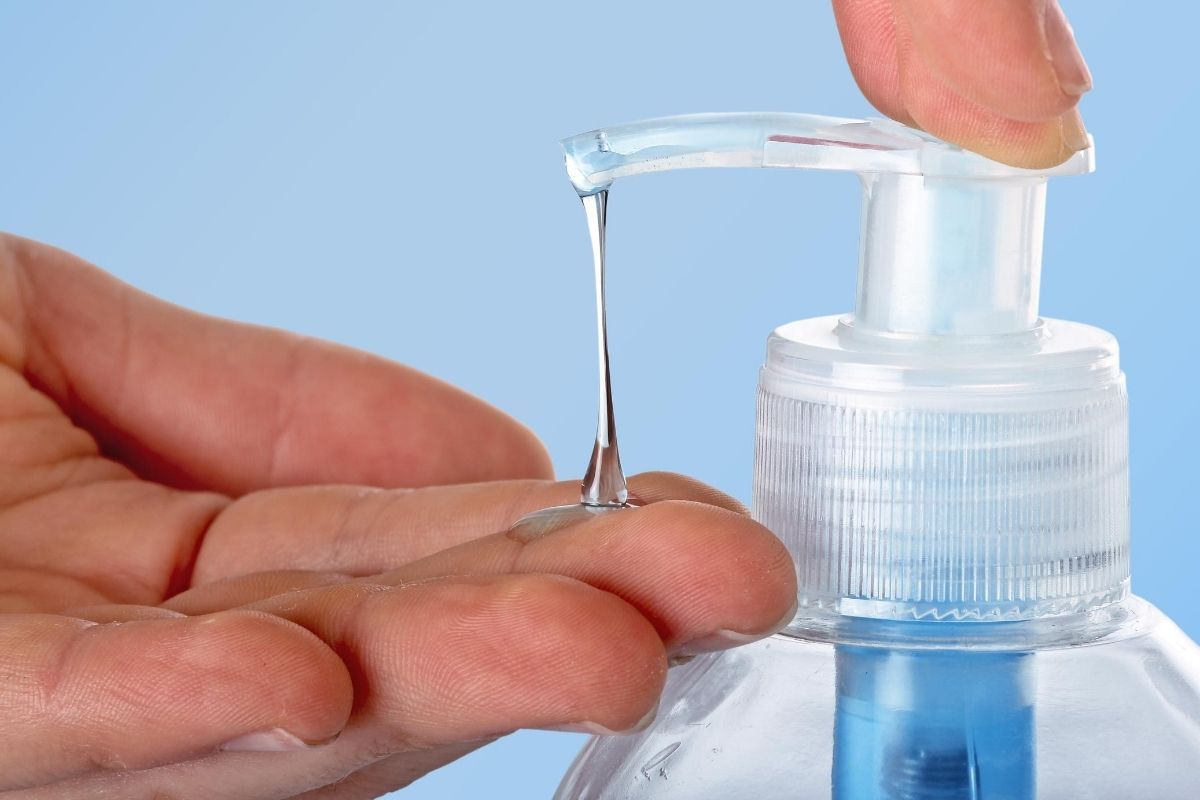

In the light of recent events regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, everyone was rushing out to buy antibacterial liquid soaps. We sold out within days.
That in itself isn’t a problem, but it made us question three things about antibacterial soaps:
-
Are they effective on bacteria and viruses?
-
Are they harmful to humans and the environment?
-
Are they more effective than regular soaps?
Hopefully, the following will supply answers to those questions.
Let's start with the basics:
What is antibacterial soap?
Every day we can be exposed to millions of bacteria and germs. To reduce the risk of getting sick or even passing these germs onto others, we use antibacterial products.
Antibacterial soap is any sanitation product with active antimicrobial ingredients. Antimicrobials are something that prevents the growth of or kills microorganisms.
There are many antibacterial hand wash and hand sanitiser products available on the market today. However, did you know that many contain several active ingredients that are unhealthy for human beings and the environment alike?
Your antibacterial hand soap may not be as harmless or as efficient as you think. Let's talk about two of the most common, harmful antibacterial ingredients; Triclosan and Triclocarban.
What Is Triclosan?
Triclosan is a chemical found in over 75% of antibacterial liquid soaps and body wash products for killing bacteria.
The use of triclosan in consumer products has become very controversial. In 2000, the American Medical Association took an official stance against the use of antimicrobials, including triclosan in consumer antibacterial soaps.
More recently, in the USA, Triclosan was banned from use in household and healthcare products by the FDA.
-
Triclosan can cause hormonal problems as well as fertility problems in humans and has linked to the early onset of puberty.
-
Triclosan can impact natural bacterial resistance.
-
Triclosan reacts with chlorine in the water to produce chloroform, a known carcinogen. (According to research carried by the Virginia Polytechnic Institute).
-
Overuse of anti bacterial products containing Triclosan encourages antibiotic resistance.
-
It also can produce toxic chlorinated dioxins in the presence of sunlight.
What is Triclocarban?
Triclocarban (TCC), a popular antimicrobial, is found in many antibacterial products.
-
TCC has links to cancer and reproductive issues in humans and animals.
-
Three-quarters of the TCC makes its way into surface water. Also into municipal sludge; frequently applied to crop fields as fertiliser in the United States. (Reference: Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health)
-
TCC contaminates an estimated 60% of streams in the U.S.
Is Antibacterial soap more effective than regular soap?
Other than the dangers mentioned above, several other things render antibacterial soap dangerous to your health.
Overuse of antibacterial products can diminish the healthy bacteria on your skin. Antibacterial soaps with harmful chemicals can remove your skin's natural oils, making skin drier.
These chemicals can perpetuate the reproduction of drug-resistant bacteria, including E. coli. Antibacterial soap is highly effective at precisely what it intends to prevent; encouraging the growth of bacteria in the human body.
Many people are using hand sanitizer as a substitute for handwashing. Hands should be washed frequently and thoroughly.
Researchers found that antibacterial soap is no more useful than washing with plain soap and water, in terms of preventing infections. Most common diseases are viral, not bacterial, and therefore cannot be checked or cured with the use of antibacterial agents.
If you for the health of your household and the environment, discard any antibacterial hand soap or body washes you have. Antibacterial soap is highly ineffective and can be very toxic to humans and the environment alike.
There are many natural products on the market that are not damaging to your health and the environment. For example, regular soaps do a better job at antibacterial resistance than consumer antibacterial soaps.
Look out natural ingredients like Aloe Vera, Rosemary, Lemon Verbena and Green Clay. All these make excellent natural antibacterial soaps but without the health risks mentioned with the above. Make sure you wash your hands correctly, though.
Et Vous?
Do you use antibacterial soaps? Or do you prefer a more natural alternative? Please leave your thoughts and comments below. You can even share this article with your friends using the antibacterial buttons below :)